Recently, the deep web has earned a reputation as a sanctuary for criminal endeavors and unchecked trade. The appeal of privacy offered by dark web markets has captivated numerous users seeking everything from both lawful and unlawful products to specialized services. Comprehending the economics at play in these hidden marketplaces requires a closer examination of their unique dynamics, the range of users involved and the elements leading to their growth.
Hidden markets operate beyond mainstream economic systems, often enveloped in a cover of anonymity. This environment encourages both innovation and danger, empowering users to maneuver through a complicated landscape of buyer-seller interactions while also facing the constant risks of law enforcement and digital offenses. Investigating the interplay between concealment, trust, and market dynamics within these environments reveals not only their charm but also the difficulties that come with them.
Market Structure of the Dark Web
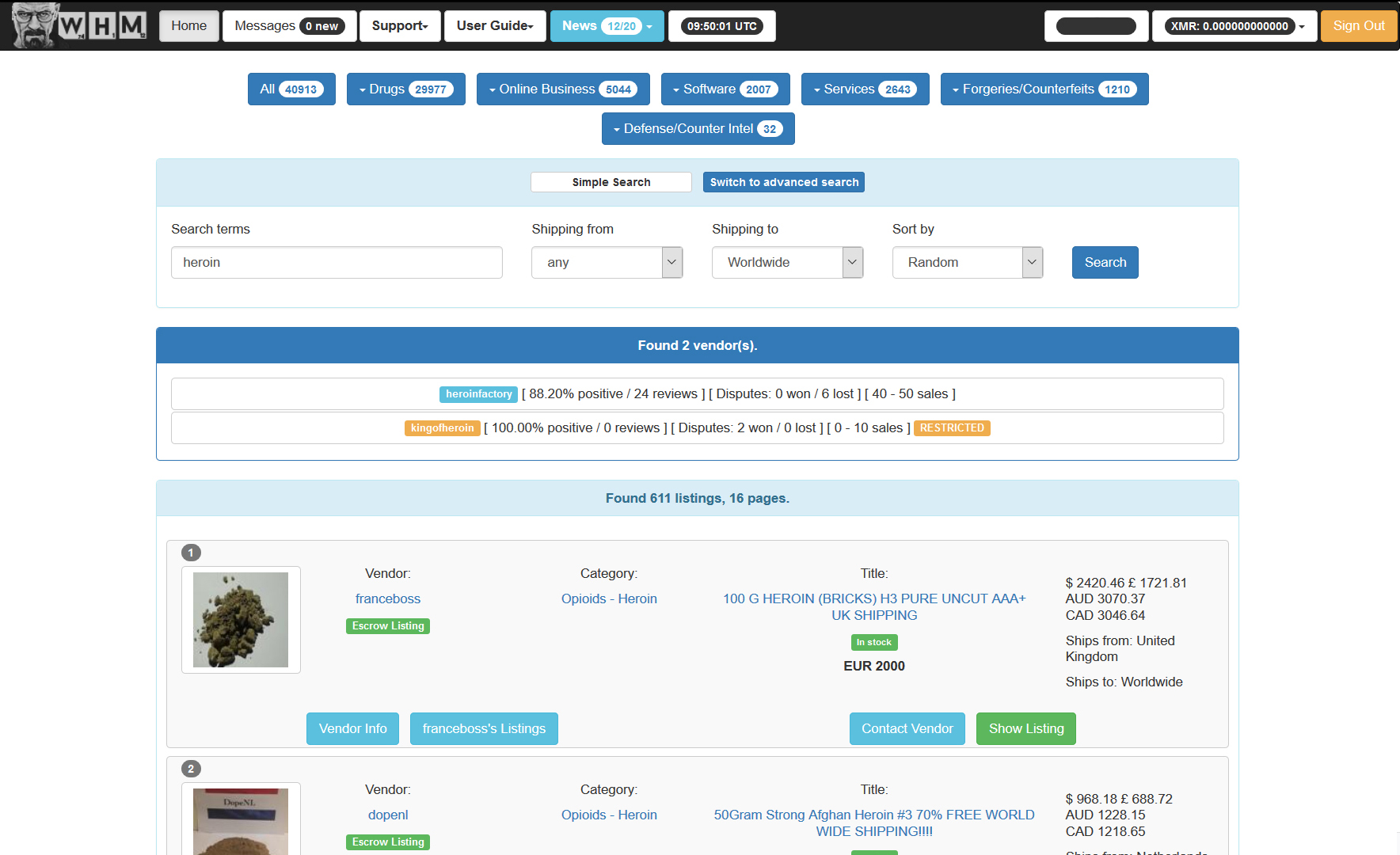
The deep web is characterized by a distinct market structure that operates outside the purview of conventional economic systems. It consists of a variety of platforms, known as black markets, where users can anonymously buy and sell a wide array of products and services. These markets function on principles of supply and demand, with offerings spanning illegal substances to hacking services, and even digital currencies. The anonymity afforded by security measures is a crucial aspect that attracts both buyers and sellers, creating a unique ecosystem driven by discretion and often illicit activities.
Within this framework, the structure of dark web markets is often decentralized. Unlike typical markets that may be dominated by a few large players, darknet markets usually comprise numerous small vendors competing for customers. This rivalry can lead to price volatility and varying quality of goods. Additionally, the use of escrow services within transactions helps to build trust among users, mitigating the threats associated with online fraud. The decentralized nature also means that when one market is shut down, others can quickly emerge, maintaining an ongoing cycle of market evolution.
The economic dynamics of the dark web are further influenced by the community and feedback mechanisms in place. dark market list , ratings, and transaction histories play a critical role in vendor trustworthiness and consumer behavior. Buyers often depend on reviews and past experiences to make educated choices, while sellers strive to build a positive reputation to attract more clients. This interconnected web of trust creates a more stable market environment, despite the inherent risks and legal consequences associated with operating in the anonymity of the dark web.
Main Participants and Contributors
Within the illicit web ecosystem, there are several major participants who drive the market dynamics. These include sellers, who are usually tasked with supplying goods and services, and customers, who aim to purchase these products. Vendors operate with diverse levels of professionalism, ranging from well-structured sellers to individuals engaging in sporadic sales. The degree to which they make use of encryption and privacy tools often affects their success and longevity in the market. Their credibility is vital, as feedback from previous transactions establishes trust and credibility in a largely unidentified environment.
Another key stakeholder is the payment processor. In darknet markets, cryptocurrencies, particularly Bitcoin, serve as the primary means of exchanges due to their concealed nature, allowing for a degree of anonymity. However, specialized services such as coin mixers and coin shufflers also appear to additionally obfuscate the transaction histories, appealing to both vendors and buyers. These processors not only enable transactions but also sometimes engage in laundering activities, which adds a dimension of complexity to the financial interactions of the dark web.
Lastly, police and regulatory agencies play a significant role as stakeholders, continuously adapting to the evolving landscape of dark web markets. Their existence creates a friction between market participants, as authorities work to disrupt illegal operations while criminals innovate ways to avoid law enforcement. This cat-and-mouse game influences the economic dynamics, impacting vendors’ operational tactics and buyers’ behaviors as they navigate risks associated with anonymity and police oversight.
Financial Forces Propelling Underground Network Transactions
The underground internet functions on a set of economic drivers that differ greatly from traditional economies. One of the most significant aspects is the anonymity given to users. This privacy attracts individuals looking to purchase or offer items and facilities that may be illegal or scrutinized in the conventional economy. The shortage of regulatory permits for cost fluctuations that can vary greatly depending on desire and supply, frequently leading in inflated prices for particular goods while maintaining others more accessible.
Furthermore, the presence of multiple cryptocurrencies as the main way of transaction fuels the underground internet marketplace. These digital currencies offer individuals a level of secrecy and safety that traditional transaction systems are unable. The volatility of digital currencies can lead to opportunistic trading actions among traders, often leading to a volatile marketplace where traders seek to profit on price variations. This situation further deepens the loop of purchasing and trading, as users endeavor to exploit the environment for monetary benefit.
Finally, the competitive quality of dark web markets encourages continual innovation among providers. Merchants often strive to set apart their offerings through service quality, user service, and special attributes. This rivalry fosters an environment where more complex items and solutions are frequently released, including increasingly formalized market models resembling conventional business models. As a result, the underground internet is not just a safe space for illegal activity but also a intricate monetary ecosystem shaped by its unique factors.

